HashMap
底层实现
Hash的实现时数组加链表
如图所示
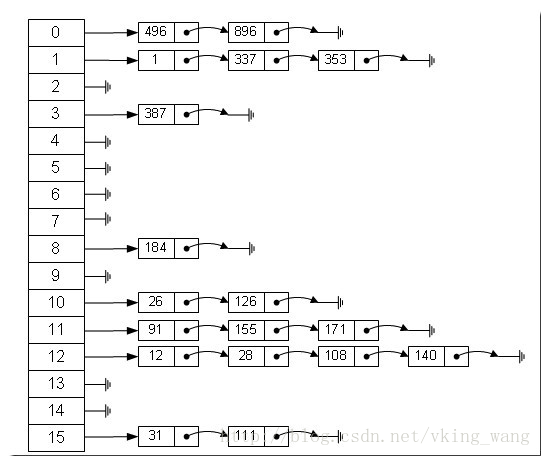
而hashMap我们每一次get 只获取 第一个值。
初始容量和负载因子##
因为put的时候可能需要做扩容,扩容会导致性能损耗,所以如果可以预知Map大小的话,可以设置合理的初始大小和负载因子来避免HashMap的频繁扩容导致的性能消耗。
默认为16与0.75
就是在插入第12(16*0.75)个的时候进行rehash
put 源码
public V put(K key, V value) {
//如果table为空
// static final Entry<?,?>[] EMPTY_TABLE = {};
// 为table 充气 想想一下 其实是扩容
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
//当key为null,调用putForNullKey方法,保存null与table第一个位置中,这是HashMap允许为null的原因
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);
//获取应该在table 中的下标
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
//遍历寻找与key相同的位置
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
//覆盖旧值并返回旧值
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
//修改次数 +1
modCount++;
//添加新的entry到i位置中
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
/**
* Adds a new entry with the specified key, value and hash code to
* the specified bucket. It is the responsibility of this
* method to resize the table if appropriate.
* 添加一个新的条目(key-value-hascode)到固定的桶,
* Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of put method.
*/
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
//如果当前的size大于阀值,并且要存的位置不为null 扩容至当前容量的2倍
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
//重新计算位置
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
/**
* Like addEntry except that this version is used when creating entries
* as part of Map construction or "pseudo-construction" (cloning,
* deserialization). This version needn't worry about resizing the table.
*
* Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of HashMap(Map),
* clone, and readObject.
* 创建条目并添加
*/
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}2017.06.25 add 几个新的1.8的api ,并且hashmap的源码底层数据结构已经变成 数组+链表+红黑树,当链表的长度大于8时转为红黑树
package com.wuhulala.javase.collection;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* author: wuhulala
* date: 2017/6/25
* version: 1.0
* description: 作甚的
*/
public class HashMapTest {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HashMapTest.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> nameAddress = new HashMap<>();
nameAddress.put("xiaoming", "杭州市滨江区");
nameAddress.put("xiaohong", "杭州市江干区");
nameAddress.put("xiaolang", "杭州市滨江区");
nameAddress.put("xiaogou", "杭州市滨江区");
nameAddress.put("daming", "杭州市西湖区");
//1.8 如果key值不存在,写入value,否则直接返回value
nameAddress.putIfAbsent("daming", "杭州市下沙区");
print(nameAddress, "daming"); //(key,value) ---> (daming,杭州市西湖区)
//1.8 如果返回的值为null则删除这个映射
//否则写入新的值
nameAddress.compute("daming", (k, v) -> {
return "杭州市萧山区";
});
print(nameAddress,"daming"); //(key,value) ---> (daming,杭州市萧山区)
//1.8 如果这个映射的value为null才写入
nameAddress.computeIfAbsent("daming", (k) -> {
return "new address";
});
print(nameAddress,"daming"); //(key,value) ---> (daming,杭州市萧山区)
//1.8 如果这个映射的value不为null,并且返回的新值也不为null才写入
nameAddress.computeIfPresent("daming", (k, v) -> {
return "new address";
});
print(nameAddress,"daming"); //(key,value) ---> (daming,new address)
//O(n)
boolean isContainedAddress = nameAddress.containsValue("new address");
System.out.println(isContainedAddress);
//1,8 Map接口默认方法
nameAddress.replace("daming", "new address","test2");
print(nameAddress,"daming"); //(key,value) ---> (daming,test2)
nameAddress.replace("daming","test3");
print(nameAddress,"daming"); //(key,value) ---> (daming,test3)
nameAddress.put("daming","test4");
print(nameAddress,"daming"); //(key,value) ---> (daming,test4)
//1.8 遍历
nameAddress.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println(key + "[" + value + "]");
});
//清空
nameAddress.clear();
}
private static void print(Map map, String key) {
logger.debug("(key,value) ---> ("+ key +"," + map.get(key) + ")");
}
}
2017.06.25 add 看到初始获取输入值最接近的2的整数次幂的值的函数tableSizeFor
tableSizeFor的功能(不考虑大于最大容量的情况)是返回大于输入参数且最近的2的整数次幂的数。比如10,则返回16。该算法源码如下:
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}详解如下:
先来分析有关n位操作部分:先来假设n的二进制为01xxx…xxx。接着
对n右移1位:001xx…xxx,再位或:011xx…xxx
对n右移2为:00011…xxx,再位或:01111…xxx
此时前面已经有四个1了,再右移4位且位与可得8个1
同理,有8个1,右移8位肯定会让后八位也为1。
综上可得,该算法让最高位的1后面的位全变为1。
最后再让结果n+1,即得到了2的整数次幂的值了。
现在回来看看第一条语句:
int n = cap - 1; 让cap-1再赋值给n的目的是令找到的目标值大于或等于原值。例如二进制1000,十进制数值为8。如果不对它减1而直接操作,将得到答案10000,即16。显然不是结果。减1后二进制为111,再进行操作则会得到原来的数值1000,即8。,如果我们for一边循环遍历或许需要1-31次,但是这个算法永远只需要4次。
该部分转自 http://www.cnblogs.com/loading4/p/6239441.html
1.8的put 也有了相应的改变
put方法调用了putVal方法put方法只是计算了一下hash值,并没有实现真正的逻辑。就像spring中的一些方法,真正做事的方法都要加上do前缀
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}我们详细看下putVal 方法
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
// 先声明些变量,但是最好声明的时候不要int n,i这种,当然这些框架代码无所谓了
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
// 判断当前table是否为空。
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// 如果hash值对应的数组位置为空,那么直接创建一个新的节点并赋值到数组对应的位置
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
// 如果hash值与key都相等的话,说明已经找到对应的插入位置返回
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
//如果当前位置的节点类型是TreeNode 说明链表已经转为了红黑树
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
// 查找应该插入的位置
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
//否则 循环链表查询当前值应当插入的位置
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
// 如果当前的容量已经大于了阈值(默认是8)
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
//转换为对应的红黑树
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
// 插入值
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
// 判断是否需要扩展容量
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
// 空实现,给子类留个口子
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}接下来 我们详细关注一下,链表是怎么转为红黑树的
final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) {
int n, index; Node<K,V> e;
// 如果表达不到树形化的条件,即当前hash表为空,或者hash表的容量还小于此阈值(MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY:64)
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
// 扩容
resize();
else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;
// 循环当前hash值对应的hash表上的链表 开始把链表的节点的类型替换为TreeNode类型,统一用hd链接起来
do {
TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null);
if (tl == null)
hd = p;
else {
p.prev = tl;
tl.next = p;
}
tl = p;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
// 如果hash表当前位置存的的值不为空
if ((tab[index] = hd) != null)
//树化table
hd.treeify(tab);
}
}树形化的真正逻辑
final void treeify(Node<K,V>[] tab) {
TreeNode<K,V> root = null;
// 遍历所有节点
for (TreeNode<K,V> x = this, next; x != null; x = next) {
next = (TreeNode<K,V>)x.next;
x.left = x.right = null;
if (root == null) {
x.parent = null;
x.red = false;
root = x;
}
else {
K k = x.key;
int h = x.hash;
Class<?> kc = null;
for (TreeNode<K,V> p = root;;) {
int dir, ph;
K pk = p.key;
if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
dir = -1;
else if (ph < h)
dir = 1;
else if ((kc == null &&
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0)
dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);
TreeNode<K,V> xp = p;
if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {
x.parent = xp;
if (dir <= 0)
xp.left = x;
else
xp.right = x;
root = balanceInsertion(root, x);
break;
}
}
}
}
//把红黑树赋值到hash表对应的位置上
moveRootToFront(tab, root);
}static <K,V> void moveRootToFront(Node<K,V>[] tab, TreeNode<K,V> root) {
int n;
if (root != null && tab != null && (n = tab.length) > 0) {
int index = (n - 1) & root.hash;
TreeNode<K,V> first = (TreeNode<K,V>)tab[index];
if (root != first) {
Node<K,V> rn;
//赋值
tab[index] = root;
//保证root是第一个节点,如果之前的第一个节点不为空的话,那么把它插入到root和root.next中间
TreeNode<K,V> rp = root.prev;
if ((rn = root.next) != null)
((TreeNode<K,V>)rn).prev = rp;
if (rp != null)
rp.next = rn;
if (first != null)
first.prev = root;
root.next = first;
root.prev = null;
}
assert checkInvariants(root);
}
}